WHAT IS DOCKER
🐳 What is Docker? A Beginner’s Guide to Containerization
In today’s fast-paced DevOps and cloud-native landscape, deploying applications quickly and reliably is a must. Whether you're a developer or a system administrator, Docker has likely become a familiar term. But what exactly is it, and why is everyone using it?
Let’s break it down in simple terms.
🚀 What is Docker?
Docker is a platform that allows you to build, ship, and run applications inside containers. These containers are lightweight, portable, and ensure that your application will run the same regardless of the environment it's in—your laptop, staging, or production.
Imagine packing all your app’s dependencies and configurations into a neat box 📦. That’s what a Docker container does.
📦 What is a Docker Container?
A Docker container is an isolated unit that packages code, runtime, system libraries, and everything else needed to run an application. Containers share the host operating system’s kernel, making them more efficient than virtual machines.
-
Starts quickly (in seconds)
-
Uses fewer resources
-
Easily reproducible across different environments
🧰 Docker vs Virtual Machines
| Feature | Docker Containers | Virtual Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Starts in seconds | Takes minutes |
| Resource Usage | Lightweight | Heavy (requires OS per VM) |
| Isolation | Process-level | Full system-level |
| Portability | Extremely portable | Limited by OS and hypervisor |
| Size | Small (MBs) | Large (GBs) |
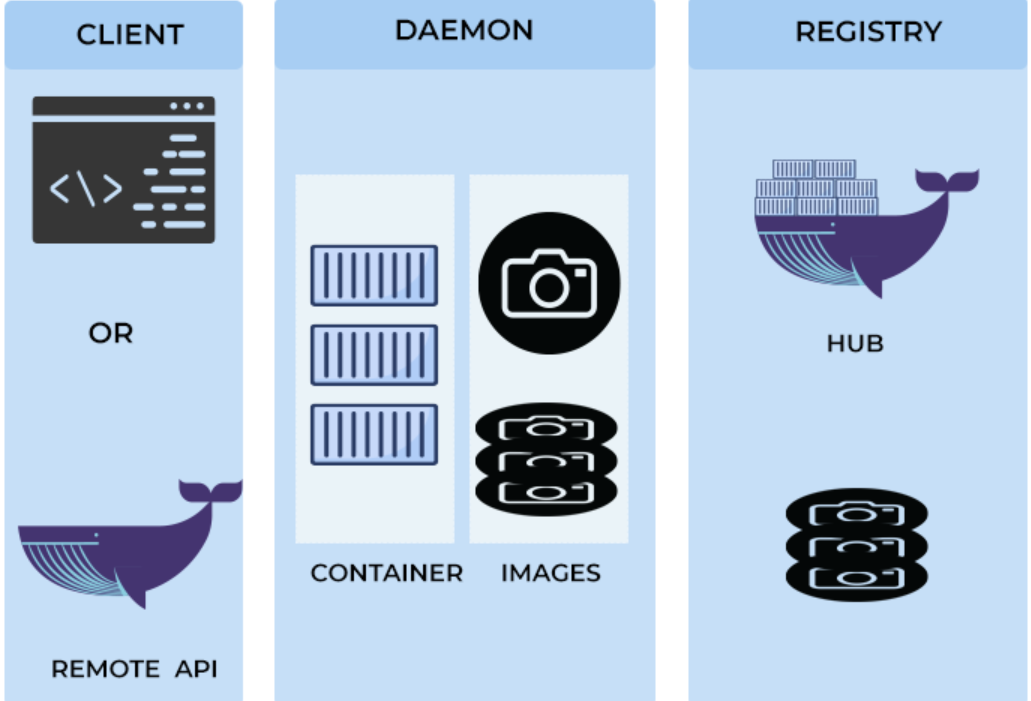
🧱 Docker Architecture
Docker uses a client-server architecture:
-
Docker Client: Sends commands (
docker run,docker build, etc.) -
Docker Daemon (dockerd): Runs in the background and handles container lifecycle
-
Docker Images: Blueprints used to build containers
-
Docker Containers: Actual running instances
-
Docker Registry: Stores and distributes images (e.g., Docker Hub)
🖥️ How to Install Docker (for Beginners)
🔹 On Windows or macOS:
-
Download Docker Desktop from https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop
-
Install and run it.
-
Use the terminal (or Docker CLI) to test:
🔹 On Ubuntu:
🧪 Quick Hands-On: Create a Dockerized Web App
Let’s create a simple Node.js app and Dockerize it.
-
Create
app.js:
-
Create
Dockerfile:
-
Build and run:
Now open http://localhost:3000 in your browser—Boom! 🎉 You’re running a containerized app!
🔒 Security and Best Practices
-
Keep images minimal (use Alpine Linux when possible).
-
Regularly scan images for vulnerabilities.
-
Avoid running containers as root.
-
Use
.dockerignoreto exclude unnecessary files.
🌍 Real-World Use Cases
-
Microservices: Isolate each service (e.g., auth, user, payments) in its own container.
-
CI/CD Pipelines: Build, test, and deploy consistently using Docker images.
-
Dev Environments: Replicate production-like environments easily on your machine.
-
Cloud Deployments: Docker is widely supported on AWS, Azure, GCP, and Kubernetes.
📚 Final Thoughts
Docker is more than just a container tool—it's a movement that’s changed how we develop, test, and deploy software. Whether you're building personal projects, managing enterprise applications, or deploying cloud-native microservices, Docker helps you work faster, safer, and more efficiently.
✨ TL;DR
-
Docker simplifies app deployment using containers.
-
Containers are lightweight, fast, and portable.
-
Perfect for modern DevOps, microservices, and cloud-native development.




Comments
Post a Comment